Reason to trust

How Our News is Made
Strict editorial policy that focuses on accuracy, relevance, and impartiality
Ad discliamer
Morbi pretium leo et nisl aliquam mollis. Quisque arcu lorem, ultricies quis pellentesque nec, ullamcorper eu odio.
As more and more businesses and processes continue to jump on the blockchain technology bandwagon to harness the potential benefits it offers, a few limitations of blockchain have come to the fore owing to its increasing use in a variety of ways. For instance, smart contract-powered Ethereum continues to face issues of scalability, security and network congestion, while Bitcoin is hit with questions about becoming a mainstream payment method.
QTUM Implements New Features
To address these challenges, QTUM, operated by the Singapore-based QTUM Foundation, was developed as a decentralized, open-source, smart contracts-powered platform and value transfer protocol. It claims to be a new-age blockchain solution that attempts to marry the salient features of the two popular cryptocurrencies – it combines Ethereum’s smart contract functionality with Bitcoin’s security.
QTUM has recently announced the launch of many new changes at the system and operational levels which are aimed at increasing the adoption of the cryptocurrency network among the masses.
The most significant update for QTUM is the development of its dedicated x86 virtual machine (VM), which will allow it to transition away from the standard Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). QTUM has been running on EVM since inception which carries a few limitations like support for only one programming language.
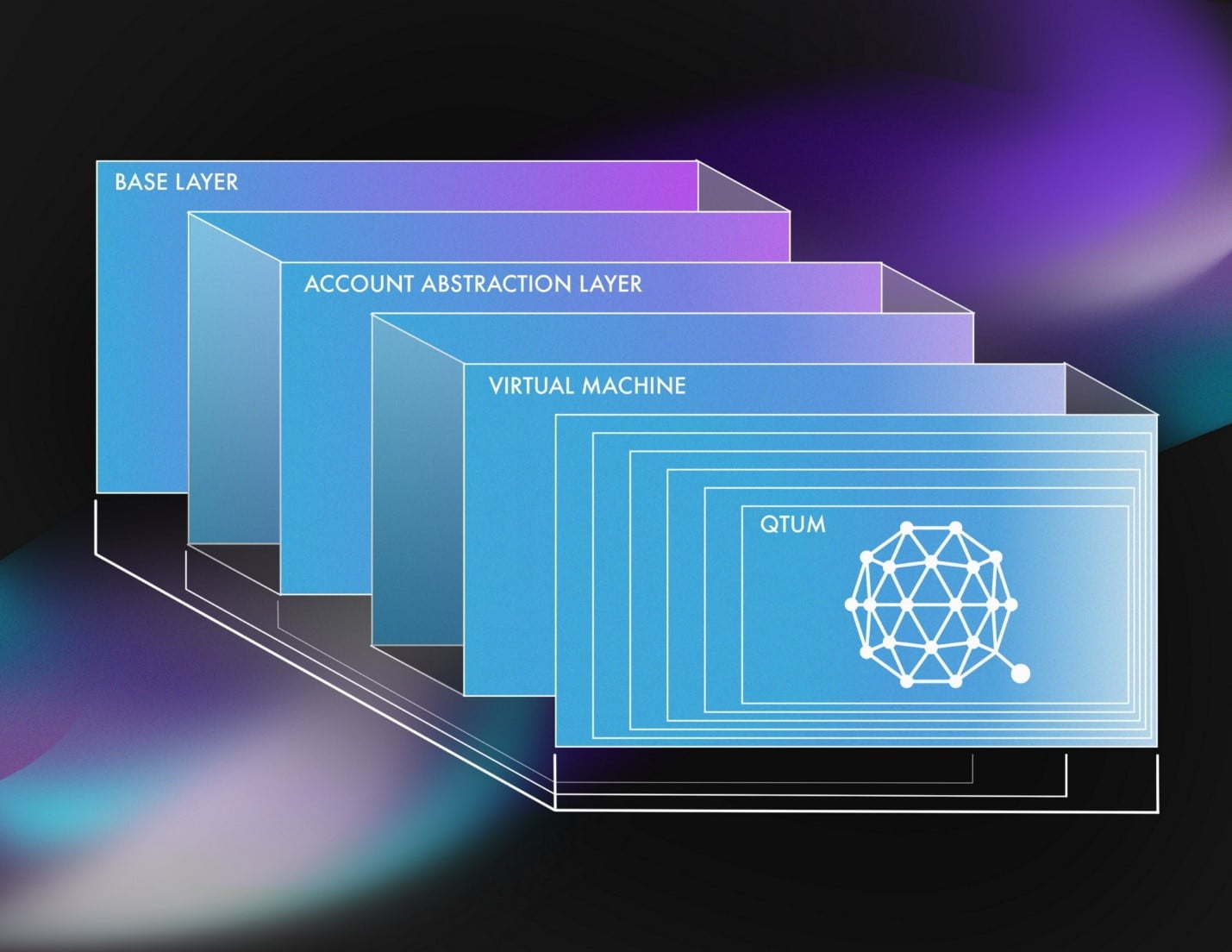
The QTUM x86 VM is a smart contract operating system built to enable easy deployment of decentralized applications (dApps). It is expected to offer major benefits which include support for multiple programming languages like C, C++ and Rust, a standard coding library, an optimized gas charging model, new possibilities for creation, execution, and management for new-age smart contracts, multiple APIs for easy plug and play, and support for alternative data storage. These enhancements are expected to make lives easy for the developers to create various apps on the QTUM network and benefit from them.
The overall working mechanism of smart contracts is set to take a new road which will make the x86 VM more scalable and will reward smart-contract developers by charging less fee in terms of the network gas. The mechanism will encourage “tight coding,” which will reward the developers to write programs that use fewer resources on the QTUM network. Essentially, the new age QTUM will act as a complete, dedicated “operating system,” saving space, resources and processing power, making the blockchain network more scalable, fast and clutter-free. According to QTUM co-founder Jordan Earls, the x86-based programs are found to be 10 to 20 percent smaller in terms of size as compared to their EVM counterparts during the initial testing.
QTUM is launching three new projects called Qx, QDex, and Qrypto which are expected to contribute to the improvement of the overall QTUM ecosystem.
Qx – a decentralized transaction protocol that will work like a trading app facilitating the trading of digital assets based on QTUM
QDex – a decentralized token exchange running on QTUM blockchain that will allow users to complete QRC token transactions through an easy to use, intuitive and concise interface offering a smooth user experience
Qrypto – Similar to Metamask, Qrypto will be a browser wallet management plug-in that will work like the necessary browser interface between blockchain and dApps.
Market Potential for QTUM
QTUM has made good strides in Asia, gaining popularity among the regional users, and is now aiming to expand to other parts of the globe.
It struck a key partnership with Chinese cybersecurity leader Qihoo 360 in January this year, which opened the doors for the QTUM foundation to join the 360 Blockchain Research Center. It will establish a blockchain lab to develop solutions for 360’s products with the blockchain flavor.
The company also has a strategic collaboration with Hong Kong-headquartered Baofeng that has a market cap of $1.2 billion on the Shenzhen Stock Market. Baofeng has 200 million active users who subscribe to high-quality video content, and the company plans to capitalize on the QTUM blockchain as the blockchain platform on which it will build a decentralized content delivery network. Another gaming company called BINGO will use QTUM blockchain to improve gaming experience and allow seamless data access and transparency between developers and game publishers in the $170 billion gaming industry.
QTUM has also found use in social media and instant messaging services. BeeChat, a popular messaging app in Asia, though lesser known in the western world, has more than two million users and is built on the foundation of QTUM blockchain. Mithril, a social media blockchain project will be developing its decentralized apps on QTUM.
While the bulk of QTUM user base has so far been confined to the Asian geography, the network has ambitious plans to expand across the globe with new features. QTUM has also announced an ambitious growth plan with a renewed marketing strategy that will help it gain more traction among global users and developers. It has already secured the coveted status of having the third largest full nodes on the global scale after Bitcoin and Ethereum, which is an indication of its increasing adoption.
QTUM has gained enough traction since its launch in the cryptocurrency market. It claims to have emerged as an efficient alternative to other top-rated blockchain-platforms like Ethereum, NEO, Cardano, and EOS. It holds the twentieth rank among the top cryptocurrencies by market capitalization as of this writing and now has the third largest set of full nodes (7,000) across the globe, after Ethereum (20,000) and Bitcoin (13,000).
The Bottom Line
QTUM seems to have rightly identified the pain-points of the existing, popular blockchain networks and is attempting to emerge as a viable solution to the challenges. While updates and new feature launches are common to the blockchain networks in the cryptocurrency world, the outcome will be realistically judged by the mass adoption numbers that will emerge over time.



















